What Is Buy Past Tense? A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding The Past Tense Of "Buy"
Understanding the past tense of "buy" is essential for mastering the English language. Whether you're a student, a professional, or someone looking to improve your grammar, knowing how to use "bought" correctly can significantly enhance your communication skills. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of the past tense of "buy," its usage, and common mistakes to avoid.
Language is a powerful tool that connects people across cultures and borders. For English learners, mastering verb tenses is one of the most important steps in becoming fluent. One common verb that often causes confusion is "buy." Specifically, its past tense form, "bought," can be tricky for those unfamiliar with irregular verbs.
This article aims to provide a detailed explanation of the past tense of "buy," including its applications in various contexts. By the end of this guide, you'll have a solid understanding of how to use "bought" effectively and confidently in your conversations and writing.
- What Denomination Is The National Cathedral
- How Do I Watch True Blood
- Forest Grove Christian Reformed Church
- Sonic Drive In Clovis
- Peliculas De Anime En Netflix
Table of Contents
- What is Buy Past Tense?
- Understanding Irregular Verbs
- How to Use "Bought" in Sentences
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Practical Examples of "Bought" in Context
- Subtleties of "Bought" vs. "Buy"
- Idioms Involving "Bought"
- The Historical Evolution of "Bought"
- Quizzes to Test Your Knowledge
- Conclusion and Next Steps
What is Buy Past Tense?
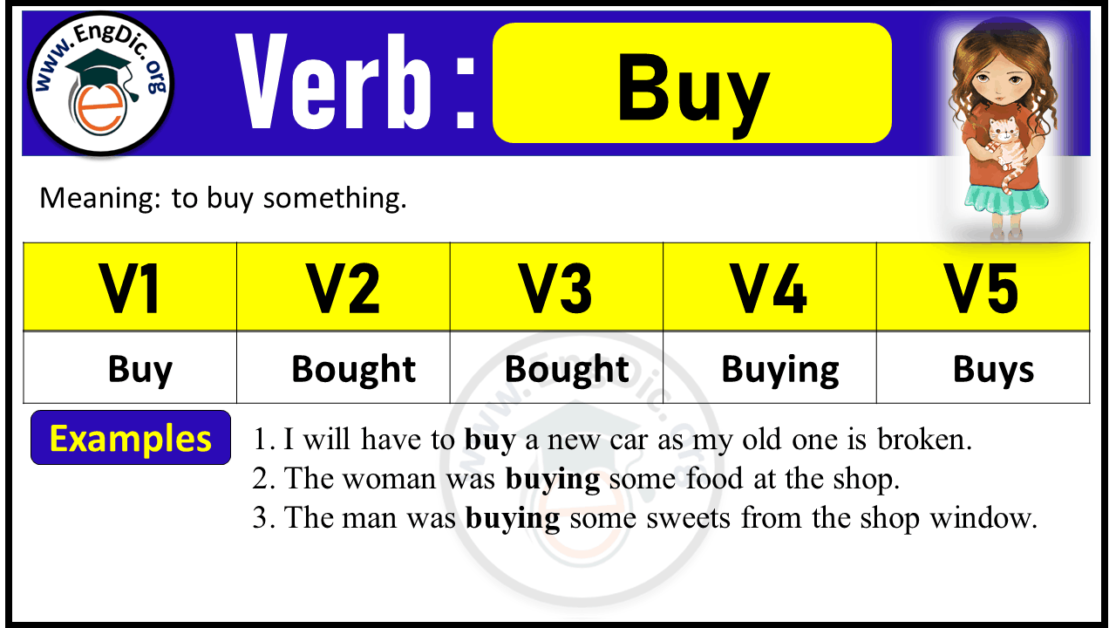
The past tense of "buy" is bought. Unlike regular verbs, which typically add "-ed" to form the past tense, "buy" is an irregular verb. This means its past tense form is unique and must be memorized. Understanding this distinction is crucial for correct usage in both spoken and written English.
Bought is used to describe actions that occurred in the past, such as purchasing items, services, or experiences. For example, "I bought a new laptop yesterday" indicates that the action of purchasing the laptop happened in the past.
It's important to note that "bought" is also the past participle of "buy," which is used in perfect tenses. For instance, "I have bought everything we need for the party" uses the present perfect tense to emphasize the completion of an action.
- Spirit Airlines Rat On Plane
- B R Auto Wrecking Chehalis
- The Lodge Breckenridge Colorado
- Easy Diy Macrame Wall Hanging
- Father Of The Daughter Wedding Speech
Understanding Irregular Verbs
Why Are Irregular Verbs Important?
Irregular verbs are a fundamental aspect of English grammar. Unlike regular verbs, which follow predictable patterns when forming past tenses, irregular verbs have unique forms that must be learned individually. "Buy" is just one example of an irregular verb, but there are hundreds of others in the English language.
- Irregular verbs are used frequently in everyday conversation.
- Mastering them improves fluency and accuracy in communication.
- They often appear in idiomatic expressions and fixed phrases.
Common Irregular Verbs
Here are some other common irregular verbs that share similarities with "buy":
- Go → Went → Gone
- Run → Ran → Run
- Speak → Spoke → Spoken
How to Use "Bought" in Sentences
Using "bought" correctly in sentences requires an understanding of its function as both a past tense and past participle verb. Below are examples of how "bought" can be applied in different contexts:
- Simple Past Tense: "She bought a new dress for the wedding."
- Present Perfect Tense: "We have bought all the ingredients for dinner."
- Past Perfect Tense: "By the time they arrived, I had already bought the tickets."
Each of these examples demonstrates how "bought" can be used to describe actions completed in the past, whether recently or long ago.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
One of the most common mistakes learners make is confusing "buy" with its past tense form, "bought." Here are a few tips to help you avoid these errors:
- Remember that "buy" is the base form and "bought" is the past tense.
- Avoid using "buyed," which is incorrect and non-standard.
- Pay attention to context clues to determine the correct verb form.
For example, saying "I buyed a book yesterday" is incorrect because the past tense should be "bought." Always double-check your verb forms to ensure accuracy.
Practical Examples of "Bought" in Context
Everyday Situations
Here are some practical examples of how "bought" is used in everyday scenarios:
- At the supermarket: "I bought some groceries for the week."
- Online shopping: "She bought a new phone online last night."
- Traveling: "We bought tickets for the train ride to Paris."
Business Context
In a business setting, "bought" might be used to describe transactions or acquisitions:
- "The company bought another startup to expand its services."
- "They bought shares in the stock market during the sale."
Subtleties of "Bought" vs. "Buy"
While "buy" and "bought" may seem straightforward, there are subtle differences in their usage that can impact meaning. For instance:
- "Buy" refers to a present or future action, such as "I will buy a car next month."
- "Bought" refers to a completed action in the past, such as "I bought a car last week."
Understanding these nuances helps ensure clarity and precision in communication.
Idioms Involving "Bought"
English is rich with idiomatic expressions, and "bought" appears in several common ones:
- "Bought the farm" - A euphemism for dying or passing away.
- "Bought into the idea" - To accept or support a concept or plan.
- "Bought time" - To delay something to gain more time.
These idioms often have figurative meanings, so it's important to study their contexts to fully understand their usage.
The Historical Evolution of "Bought"
The word "bought" has its roots in Old English, where it was spelled "gebyt." Over time, the spelling and pronunciation evolved to become the modern "bought." This evolution reflects the dynamic nature of language and how words adapt to cultural and societal changes.
Studying the history of words like "bought" provides valuable insights into the development of the English language and its relationship with other languages, such as German and Dutch.
Quizzes to Test Your Knowledge
Test your understanding of "bought" with these quick quizzes:
- Which is the correct past tense of "buy"?
- A) Buyed
- B) Bought
- C) Buied
- A) I buyed a new book yesterday.
- B) She bought a new dress for the party.
- C) They buy tickets for the concert.
Answers: 1) B, 2) B
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, understanding the past tense of "buy" is a vital step in mastering English grammar. By familiarizing yourself with "bought" and its various applications, you can improve your communication skills and avoid common mistakes. Remember to practice regularly and seek out opportunities to use "bought" in real-life situations.
We encourage you to share this article with others who might find it helpful and leave a comment below with any questions or feedback. For further reading, explore our other articles on grammar and language learning. Together, let's continue to grow and improve!
- Why Is Russia Not In The Olympics But Israel Is
- Costco Near Amarillo Tx
- Are Carp And Koi The Same
- Pizza Brew Scarsdale
- Gkn Bowling Green Ohio

Past Tense Of Run, Past Participle Form of Run, Run Ran Run V1 V2 V3
Buy Past Tense Archives EngDic

Buy Past Tense Verb Forms, Conjugate BUY