Does The Sun Rotate Clockwise Or Counterclockwise? A Comprehensive Guide
Have you ever wondered whether the Sun rotates clockwise or counterclockwise? The Sun, the center of our solar system, is not just a static celestial body but a dynamic star that undergoes various fascinating processes. Understanding its rotation can provide deep insights into how our solar system functions and evolves over time.
As one of the most studied celestial objects, the Sun's rotation has been a subject of scientific inquiry for centuries. Its rotation plays a crucial role in phenomena such as solar flares, sunspots, and magnetic field generation. In this article, we will explore the Sun's rotation pattern, its significance, and how it impacts the solar system.
This article is designed to provide a detailed, scientific explanation of the Sun's rotation, making it accessible to readers of all backgrounds. Whether you're a student, a science enthusiast, or simply curious about the universe, this guide will answer your questions and expand your knowledge.
- City Of Milwaukee Recycling Pickup
- Bahama House Daytona Shores
- Keto And Cream Cheese
- Cavinder Twins Sports Illustrated
- Is Damon Wayans Jr Married
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Biography of the Sun
- Does the Sun Rotate Clockwise or Counterclockwise?
- Rotation at the Solar Equator
- Rotation Near the Solar Poles
- Understanding Differential Rotation
- Impact of Sun's Rotation on the Solar System
- Sunspots and Solar Rotation
- Role in Magnetic Field Generation
- Scientific Research on Sun's Rotation
- Conclusion
Biography of the Sun
The Sun, a nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, is the heart of our solar system. It accounts for about 99.8% of the total mass of the solar system and provides the energy necessary for life on Earth. Below is a brief overview of the Sun's key characteristics:
Sun's Key Data
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| Age | Approximately 4.6 billion years |
| Mass | 1.989 × 10³⁰ kg |
| Diameter | About 1.39 million kilometers |
| Surface Temperature | Approximately 5,500°C |
| Core Temperature | Approximately 15 million°C |
| Rotation Period | Varies based on latitude |
Does the Sun Rotate Clockwise or Counterclockwise?
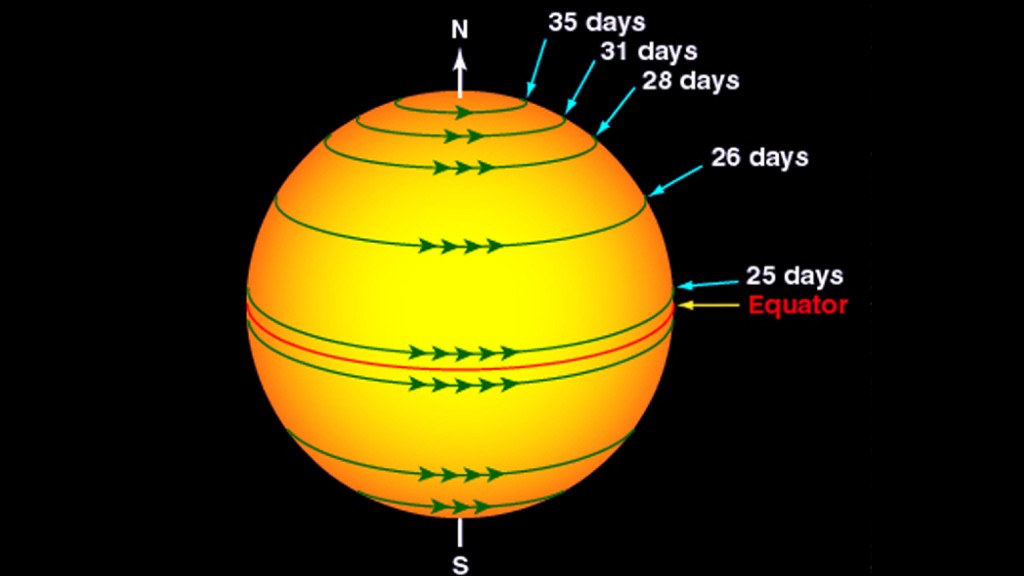
The Sun rotates on its axis, but its rotation pattern is not uniform. Unlike solid objects, the Sun is a ball of plasma, and its rotation varies depending on the latitude. Observations show that the Sun rotates counterclockwise when viewed from above its north pole. However, this rotation is not consistent across all regions of the Sun.
Key Factors Influencing Sun's Rotation
- Equatorial Region: The Sun rotates faster at the equator, completing one full rotation approximately every 25 days.
- Polar Regions: Near the poles, the rotation is slower, taking about 36 days to complete a full cycle.
- Differential Rotation: The varying speeds of rotation across different latitudes result in what scientists call "differential rotation."
Rotation at the Solar Equator
At the solar equator, the Sun rotates approximately every 25 days. This region experiences the fastest rotation due to the Sun's differential rotation phenomenon. The rapid rotation at the equator contributes to the formation of sunspots and solar flares, which are more common in this area.
- Rack Room Shoes Cary Nc
- Who Is The Quarterback For Texans
- The Wild Robot Gross
- Viola Agnes Neo Soul Cafe
- Black Hills Energy Bill Pay Online
Rotation Near the Solar Poles
Near the poles, the Sun rotates much slower, taking about 36 days to complete a full rotation. The slower rotation in these regions is due to the Sun's gaseous composition and the influence of magnetic fields. This variation in rotation speed is a key characteristic of the Sun's behavior.
Understanding Differential Rotation
Differential rotation refers to the phenomenon where different parts of the Sun rotate at different speeds. This occurs because the Sun is not a solid object but a ball of plasma. The varying rotation speeds create complex interactions within the Sun, influencing its magnetic fields and solar activity.
Causes of Differential Rotation
- Plasma Composition: The Sun's gaseous state allows for uneven rotation patterns.
- Magnetic Fields: The Sun's magnetic fields play a significant role in shaping its rotation dynamics.
- Gravitational Forces: Internal gravitational forces contribute to the differential rotation observed in the Sun.
Impact of Sun's Rotation on the Solar System
The Sun's rotation has a profound impact on the entire solar system. It influences solar wind patterns, magnetic fields, and the behavior of planets and other celestial bodies. Understanding the Sun's rotation is essential for predicting space weather and its effects on Earth.
Key Effects of Sun's Rotation
- Solar Wind: The Sun's rotation drives the solar wind, a stream of charged particles that affects the entire solar system.
- Magnetic Storms: Variations in the Sun's rotation can lead to magnetic storms that disrupt satellite communications and power grids on Earth.
- Planetary Orbits: The Sun's rotation indirectly influences the orbits of planets and other objects in the solar system.
Sunspots and Solar Rotation
Sunspots are temporary phenomena on the Sun's surface that appear darker than the surrounding areas. They are caused by intense magnetic activity and are closely related to the Sun's rotation. As the Sun rotates, sunspots move across its surface, providing valuable data for scientists studying solar activity.
Importance of Sunspots
- Solar Cycle Indicators: Sunspots are key indicators of the Sun's 11-year solar cycle.
- Magnetic Field Insights: Studying sunspots helps scientists understand the Sun's magnetic field and its effects on Earth.
Role in Magnetic Field Generation
The Sun's rotation plays a critical role in generating its magnetic field. The differential rotation and convection currents within the Sun create a dynamo effect, producing a complex magnetic field that extends far beyond the Sun's surface. This magnetic field influences solar activity and space weather.
Significance of the Sun's Magnetic Field
- Solar Flares: Magnetic field disruptions can lead to solar flares, which release massive amounts of energy into space.
- Auroras: The Sun's magnetic field interacts with Earth's atmosphere, causing beautiful auroras in polar regions.
Scientific Research on Sun's Rotation
Scientists have been studying the Sun's rotation for centuries, using advanced telescopes and space missions to gather data. Modern research focuses on understanding the Sun's internal dynamics, magnetic fields, and their effects on the solar system.
Notable Studies and Discoveries
- SOHO Mission: The Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) has provided valuable insights into the Sun's rotation and magnetic activity.
- Parker Solar Probe: Launched in 2018, this mission aims to study the Sun's outer atmosphere and its effects on space weather.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Sun rotates counterclockwise when viewed from above its north pole, with varying speeds depending on latitude. This differential rotation plays a crucial role in shaping the Sun's magnetic fields and influencing solar activity. Understanding the Sun's rotation is essential for predicting space weather and its effects on Earth.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments section below. For more fascinating insights into the universe, explore our other articles on astronomy and space science. Together, let's continue to unravel the mysteries of the cosmos!
- The Ups Store Amherst
- Walt Disney World Aurora
- When Is Jenni Rivera S Birthday
- Why Is Russia Not In The Olympics But Israel Is
- Cast Your Anxiety On The Lord

Does The Earth Orbit Around Sun Clockwise Or Counterclockwise The
Left and Right Rotate Icon Vector. Counterclockwise and Clockwise
Does the sun rotate? Science of solar rotation Space