World Map 2000 BCE: Exploring Ancient Civilizations And Their Geographical Context
Imagine a world map that transports you 4,000 years into the past, where ancient civilizations thrived and shaped the course of human history. The world map 2000 BCE is not just a geographical representation but a window into the lives, cultures, and advancements of early societies. This era marked significant developments in agriculture, governance, and technology, laying the foundation for modern civilization.
Understanding the world map 2000 BCE is crucial for historians, archaeologists, and enthusiasts alike. It offers insights into the geographical distribution of early societies, their trade routes, and their interactions with neighboring regions. By exploring this map, we can appreciate the complexity of ancient civilizations and their lasting impact on today's world.
As we delve deeper into the subject, we will examine the geographical landscape of 2000 BCE, the major civilizations that existed during this period, and the factors that influenced their growth and development. Join us on this journey through time as we uncover the mysteries of the ancient world.
- New Castle News Police Reports
- Forest Grove Christian Reformed Church
- New York City Police Department 94th Precinct
- What Does Putting An Onion In Your Sock Do
- How Do I Apply Concealer And Foundation
Table of Contents
- Geographical Overview of the World in 2000 BCE
- Major Civilizations Around 2000 BCE
- Mesopotamia: The Cradle of Civilization
- Egypt: A Land of Pyramids and Power
- Indus Valley Civilization: Urban Planning and Trade
- Ancient China: The Dawn of Bronze Age
- Trade Routes in 2000 BCE
- Environmental Factors Shaping Civilizations
- Technological Advancements in 2000 BCE
- Conclusion: Reflecting on the World Map 2000 BCE
Geographical Overview of the World in 2000 BCE
The world map 2000 BCE provides a snapshot of the Earth's geography during a transformative period in human history. This era saw the rise of several powerful civilizations, each occupying distinct regions with unique environmental conditions. The Fertile Crescent in the Middle East, the Nile Valley in Africa, the Indus Valley in South Asia, and the Yellow River basin in East Asia were among the most prominent areas of human settlement.
Key geographical features during this time included vast deserts, fertile river valleys, and expansive mountain ranges. These natural landscapes played a pivotal role in shaping the development of early societies. For instance, the Nile River's annual flooding ensured rich soil for agriculture, while the Tigris and Euphrates rivers provided water and transportation for Mesopotamian cities.
Major Civilizations Around 2000 BCE
Several major civilizations thrived around 2000 BCE, each contributing to the cultural and technological advancements of the time. These civilizations were interconnected through trade, diplomacy, and sometimes conflict. Below is a list of the most significant civilizations:
- Smallest Tank In The World
- Alamance Crossing Burlington Nc
- Peliculas De Anime En Netflix
- Bw3 Specials On Tuesday
- Sonic Drive In Clovis
- Mesopotamia
- Egypt
- Indus Valley Civilization
- Ancient China
- Minoan Civilization
Each of these civilizations had its own unique characteristics, but they shared common goals such as securing resources, expanding territory, and developing complex social structures.
Mesopotamia: The Cradle of Civilization
Geography and Settlements
Mesopotamia, located between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, was home to some of the earliest known cities, including Uruk, Ur, and Babylon. The fertile land supported agriculture, which became the backbone of the Mesopotamian economy. Archaeological evidence suggests that the region was densely populated, with cities serving as hubs of trade and governance.
Cultural Achievements
Mesopotamia is credited with numerous cultural and technological advancements. The invention of writing, known as cuneiform, revolutionized record-keeping and communication. Additionally, the development of the wheel facilitated transportation and trade. Religion played a central role in Mesopotamian life, with temples and ziggurats serving as focal points of spiritual and civic activities.
Egypt: A Land of Pyramids and Power
Pharaonic Rule and Architecture
Egypt in 2000 BCE was under the rule of powerful pharaohs who oversaw the construction of monumental structures such as the pyramids. These architectural marvels not only symbolized the pharaohs' divine authority but also showcased the Egyptians' advanced engineering skills. The Great Pyramid of Giza, built during this period, remains one of the most iconic structures in human history.
Agriculture and Trade
The Nile River was the lifeline of ancient Egypt, providing water, fertile soil, and transportation routes. Egyptian farmers cultivated crops such as wheat and barley, which supported a growing population. Trade networks extended across the Mediterranean and into the Arabian Peninsula, enabling the exchange of goods like gold, spices, and textiles.
Indus Valley Civilization: Urban Planning and Trade
Urban Centers and Infrastructure
The Indus Valley Civilization, located in present-day Pakistan and India, was renowned for its advanced urban planning. Cities like Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa featured grid-like street layouts, sophisticated drainage systems, and multi-story buildings. These innovations reflect the civilization's emphasis on order and efficiency.
Economic Activities
Trade was a cornerstone of the Indus Valley economy, with goods such as beads, pottery, and textiles being exchanged across long distances. Evidence suggests that the civilization engaged in maritime trade with Mesopotamia and other regions. However, the exact reasons for the decline of the Indus Valley Civilization remain a subject of debate among historians.
Ancient China: The Dawn of Bronze Age
Technological Innovations
Around 2000 BCE, ancient China entered the Bronze Age, marked by the development of bronze tools and weapons. This technological advancement enhanced agricultural productivity and military capabilities. The Erlitou culture, centered in the Yellow River basin, is often cited as one of the earliest Bronze Age societies in China.
Religion and Society
Religious beliefs in ancient China were closely tied to ancestor worship and nature spirits. Rituals and ceremonies played a significant role in daily life, reinforcing social hierarchies and cultural traditions. The emergence of writing, known as oracle bone script, facilitated communication and record-keeping.
Trade Routes in 2000 BCE
Connecting Civilizations
Trade routes in 2000 BCE facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies between distant regions. The Silk Road, although not fully established at this time, had early precursors that connected Asia with the Middle East and Europe. Maritime routes along the Indian Ocean and Mediterranean Sea also enabled the movement of goods such as spices, metals, and textiles.
Cultural Exchange
Trade was not only about economic transactions but also about cultural exchange. Artifacts from one region often found their way into another, reflecting the interconnectedness of ancient civilizations. This exchange of ideas contributed to the development of new technologies, artistic styles, and social practices.
Environmental Factors Shaping Civilizations
Environmental conditions played a crucial role in shaping the growth and decline of ancient civilizations. Climatic changes, such as droughts or floods, could disrupt agricultural production and lead to societal instability. Natural disasters like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions also posed significant challenges to early societies. Understanding these environmental factors helps us appreciate the resilience and adaptability of ancient peoples.
Technological Advancements in 2000 BCE
Innovations in Agriculture
Agricultural advancements during this period included the development of irrigation systems, plows, and crop rotation techniques. These innovations increased food production, allowing for larger populations and more complex societies. The domestication of animals for labor and transportation further enhanced agricultural efficiency.
Construction and Engineering
Construction techniques improved significantly during this era, with the use of stone, brick, and mortar becoming more widespread. Engineering projects such as dams, canals, and roads facilitated economic growth and urbanization. These developments underscore the ingenuity and resourcefulness of ancient civilizations.
Conclusion: Reflecting on the World Map 2000 BCE
In conclusion, the world map 2000 BCE offers a fascinating glimpse into the lives of ancient civilizations and their achievements. From the fertile valleys of Mesopotamia to the majestic pyramids of Egypt, each region contributed uniquely to the tapestry of human history. By studying this period, we gain valuable insights into the factors that shaped early societies and their enduring legacy.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments section below. Additionally, explore other articles on our site to deepen your understanding of ancient history and its relevance to our modern world. Together, let's continue to unravel the mysteries of the past!
- Candlewood Suites Greenville Greenville
- Marshall Mi Holiday Inn Express
- Can You Bring Medications On A Plane
- Easy Diy Macrame Wall Hanging
- When Was Steven Tyler Born

The world map (2000 BC) Vivid Maps

The world map (2000 BC) Vivid Maps
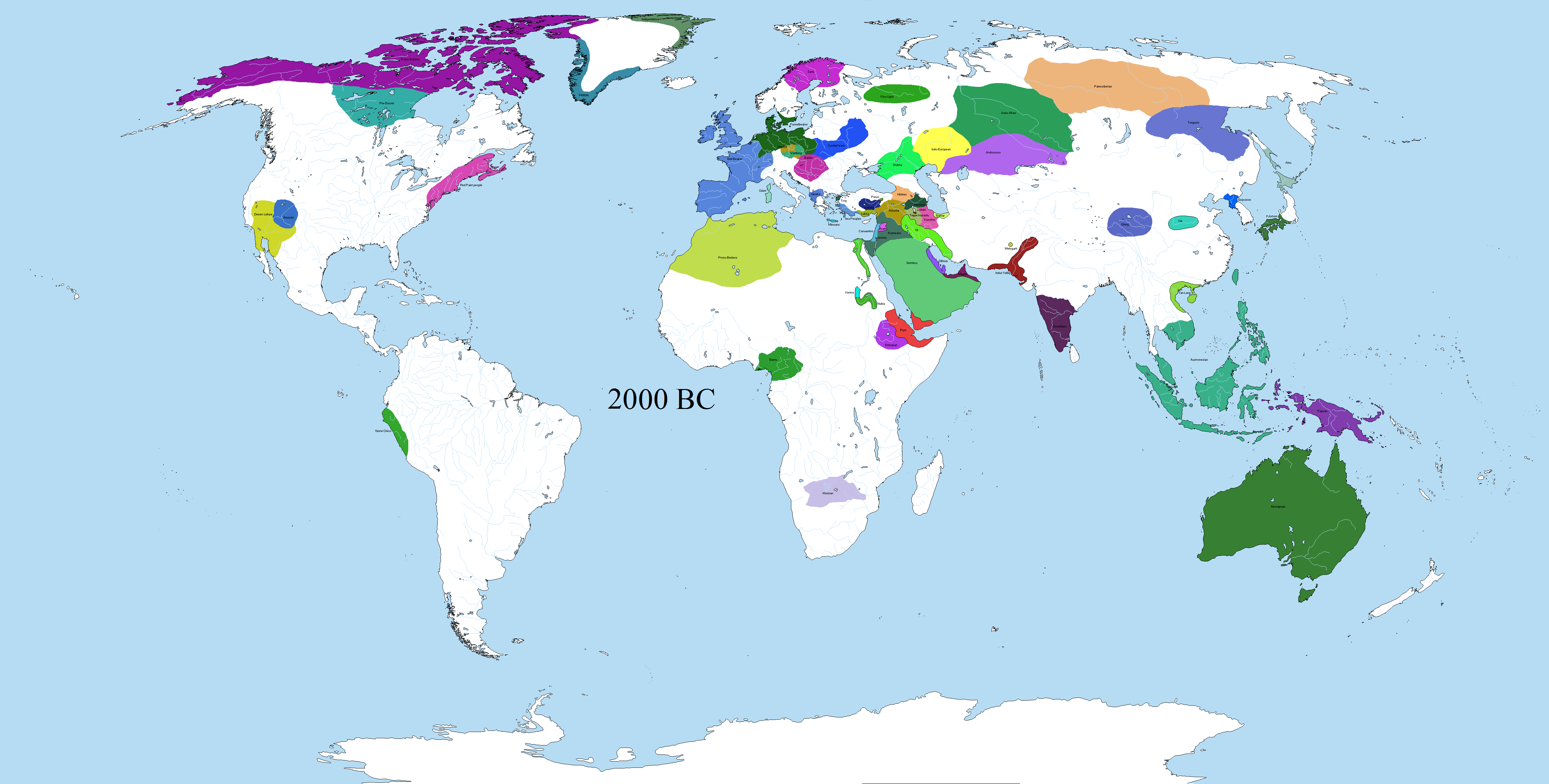
Overview Map Of The World In The Mid 2000 BC, Colorcoded, 52 OFF